Is sugar addictive? This intriguing question has sparked considerable debate among researchers and health enthusiasts alike. While substances like alcohol and nicotine have defined clinical classifications for addiction, sugar complicates the discussion with its widespread use in everyday diets. Sugar cravings often emerge because processed foods, laden with added sugars, are designed to be irresistible, leading to habitual consumption that mimics addiction-like behaviors. Understanding the health effects of sugar and monitoring our sugar consumption limits is essential for maintaining a balanced diet, particularly as the average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily.
When discussing the concept of sugar addiction, it’s important to consider alternative terms such as sugar dependency and craving for sweets. Many individuals find themselves drawn to sugary treats, and this attraction often stems from the palatable nature of processed foods rich in added sugars. Despite ongoing discussions surrounding the classification of sugars as addictive substances, the reality of sugar-induced cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms cannot be overlooked. This sensation highlights the need for awareness regarding sugar intake and its influence on our health. Ultimately, examining the balance between enjoyment and moderation can help individuals navigate their relationship with sweetness.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Impacts
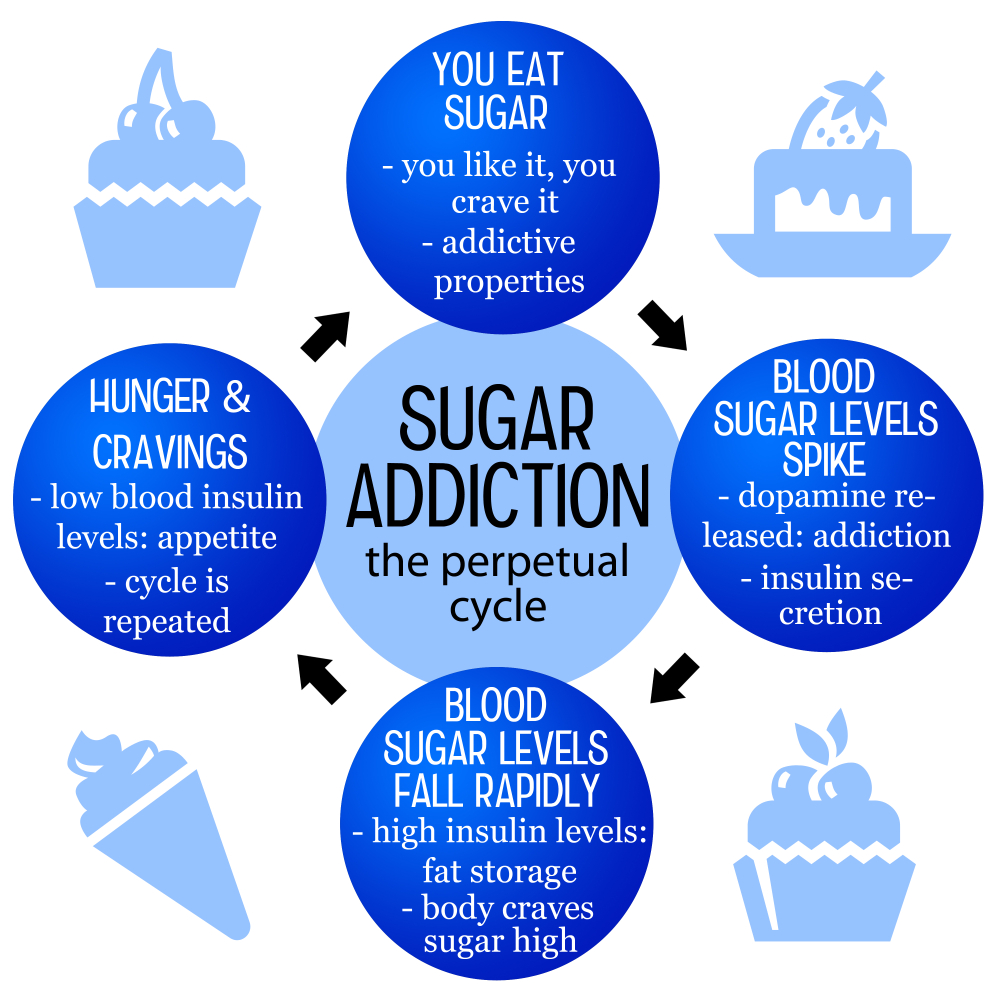
Sugar cravings are a common phenomenon experienced by many individuals, and they stem from both physiological and psychological factors. When we consume foods high in sugar, the brain releases dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This creates a cycle where the brain starts to crave more sugar to achieve those pleasurable feelings. Over time, regular consumption of sugary foods can lead to a heightened sensitivity to sugar, often making it difficult for individuals to resist these cravings despite their desire to reduce their sugar intake.
In addition, the health effects of sugar cannot be overstated. High sugar consumption is linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Processed foods laden with added sugars contribute significantly to these problems, as they are easily accessible and often more palatable than healthier options. Therefore, understanding and managing sugar cravings is essential for maintaining a balanced diet and overall health.
Is Sugar Addictive? The Controversy Explained
The question of whether sugar is addictive remains a topic of heated debate among nutrition experts. While it can induce cravings similar to those triggered by addictive substances like alcohol or nicotine, clinical criteria do not officially classify sugar as an addictive substance. Research indicates that sugar can lead to compulsive eating behaviors and withdrawal-like symptoms when severely restricted, which complicates the narrative. This has led some researchers to suggest that sugar possesses certain addictive qualities, albeit not to the same extent as drugs.
Moreover, we must consider the context in which sugar is consumed. Unlike addictive drugs that can be completely eliminated from one’s diet, sugar is naturally present in many healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Thus, moderation becomes key. The American Heart Association recommends specific sugar consumption limits—9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women—to mitigate potential adverse health effects while still enjoying the necessary sweetness that enhances our meals.
Ultimately, recognizing the addictive aspects of sugar may serve as a warning but should not lead individuals to vilify it entirely. Instead, focusing on informed consumption and maintaining a balanced diet is a healthier approach.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Consumption
Processed foods play a significant role in the increasing levels of sugar consumption among populations. These foods often come loaded with high amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them incredibly appealing. The convenience and accessibility of these snacks often override more nutritious choices, leading to habitual consumption. Consequently, individuals may find themselves consuming far more sugar than they realize, often through sugary beverages, snacks, and sweets.
Furthermore, the processing involved in these foods diminishes their nutritional benefits, resulting in a diet that lacks essential nutrients while being high in empty calories. As people become accustomed to the sweet flavors of processed foods, their sensitivity to natural sugars found in whole foods diminishes. This can perpetuate a cycle of overconsumption, contributing to the negative health effects linked to excessive sugar intake.
Health Effects of Excess Sugar Consumption
The health effects of consuming excess sugar are profound and well-documented. Regular high intake of added sugars can lead to severe health conditions such as obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. The American Heart Association has flagged excessive sugar consumption as a significant public health concern, emphasizing the need for people to be mindful of their sugar intake. Sweetness enhances the flavor of many foods, but when sugar is consumed in excess, it can lead to detrimental health outcomes.
Additionally, excess sugar consumption is linked to increased risk factors for heart disease. It can lead to higher triglyceride levels, increased blood pressure, and inflammation—all contributing factors to cardiovascular problems. Understanding the health effects associated with sugar is crucial for making more informed dietary choices and promoting better long-term health outcomes.
Gradually Reducing Sugar Intake for Better Health
For those looking to reduce their sugar intake, a gradual approach is often the most effective strategy. Abrupt elimination of sugars from one’s diet can lead to unwanted withdrawal symptoms, including headaches and cravings, which may result in returning to old eating habits. Instead, slowly decreasing the intake of added sugars allows the palate to adjust while reducing the risk of experiencing intense cravings.
Key strategies to cut back on sugar include reading nutrition labels for added sugars in processed foods, opting for natural sweeteners, and incorporating more whole foods into the diet. People should also be encouraged to find satisfying alternatives to their sugary snacks, which can help in managing cravings without feeling deprived. Overall, making small yet consistent changes can lead to significant health improvements over time.
Mindful Eating: Cultivating Healthier Habits
Mindful eating is an approach that encourages individuals to be more aware of their eating habits and the foods they consume, providing an important tool in reducing sugar intake. By paying attention to hunger cues and savoring food, individuals can reconnect with the sensory experience of eating and recognize when they are truly hungry versus eating out of habit or emotional triggers. This heightened awareness can lead to more informed decisions about food choices, particularly when it comes to sugar-laden options.
Practicing mindfulness can also help individuals resist cravings for sugary foods by promoting healthier alternatives. Focusing on the nutritional value and flavor of whole foods can enhance satisfaction and reduce the desire for processed sugary snacks. Cultivating healthier eating habits through mindfulness not only aids in reducing sugar consumption but also fosters a more positive relationship with food.
The Importance of Food Labels in Sugar Awareness
Food labels play a crucial role in increasing awareness about sugar consumption. For individuals wanting to manage their sugar intake, familiarizing themselves with how to read food labels is essential. Labels provide valuable information on added sugars in products, allowing consumers to make informed choices about what they are putting into their bodies. Being aware of the sugar content in processed foods can significantly influence dietary habits and help in curbing excess sugar consumption.
Moreover, understanding the difference between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars is vital. Often, people may overlook the cumulative effect of various sources of sugar in their diet due to a lack of awareness. By actively reading labels and monitoring their daily intake, individuals can better control their sugar consumption, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes and aligning with the recommended sugar consumption limits.
Sugar Consumption Limits: Recommendations for a Balanced Diet
To maintain a healthy lifestyle, adhering to sugar consumption limits is key. The American Heart Association has set clear recommendations for added sugars: no more than 9 teaspoons (36 grams) for men, 6 teaspoons (25 grams) for women, and even less for children. Meeting these guidelines can help stave off the adverse health effects that arise from excessive sugar intake, including weight gain, diabetes, and heart disease. Understanding and implementing these limits are crucial steps for individuals seeking to improve their overall diet.
Incorporating a diverse and balanced diet rich in whole foods can help manage sugar levels effectively. By focusing on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, individuals can naturally satisfy their sweet cravings while remaining within the recommended consumption limits. Achieving a healthy balance requires planning and commitment to dietary choices, leading to improved long-term health and wellbeing.
Enjoying Sweetness Without the Guilt
Enjoying sweetness in our diets doesn’t necessarily mean indulging in large amounts of added sugars. Learning to appreciate the natural sweetness found in fruits can provide the satisfaction our taste buds crave without the negative health effects linked to excessive added sugar consumption. Additionally, exploring healthier substitutes for traditional sugary snacks can enhance meals and snacks without the guilt of consuming processed sugars.
It is crucial to shift the perspective of sugar from an outright enemy to something that can be enjoyed mindfully and in moderation. When approached with this mindset, individuals can still experience the joy of sweetness in their lives while minimizing potential health risks. Ultimately, the goal should be to find a balance where sweetness enhances flavor and satisfaction without compromising overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive and does it lead to sugar cravings?
The debate about sugar’s addictiveness is complex. While sugar can increase cravings and encourage compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Many people experience cravings for sugar, especially from ultra-processed foods that contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to various health problems, including obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Although sugar itself is not classified as addictive, the compulsive desire to consume sugary foods can result in withdrawal-like symptoms when intake is suddenly reduced, such as headaches and anxiety.
How does the consumption of processed foods relate to sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar, which increase their palatability and may lead to addiction-like behaviors. As these foods are easily accessible, they can trigger cravings and lead to habitual consumption, making it harder for individuals to moderate their sugar intake.
What are the recommended sugar consumption limits to avoid addiction-like symptoms?
The American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons of added sugar per day for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and less for children. Keeping sugar intake within these limits can help prevent negative health effects and reduce the likelihood of developing sugar cravings.
Is reducing sugar consumption similar to overcoming an addiction to sugar?
While reducing sugar intake can result in cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms, it is not as severe as those experienced with true addictive substances. People are encouraged to lower sugar consumption gradually to avoid potential backlash from abrupt changes in diet.
Are there any sugar substitutes that can help manage sugar cravings?
Using sugar substitutes can help satisfy sweet cravings without the associated health risks of excessive sugar intake. However, it is important to choose substitutes wisely and maintain a balanced diet that prioritizes whole foods.
Can sugar have benefits in our diet despite its addictive properties?
Yes, sugar in moderate amounts can enhance flavor and contribute to overall enjoyment of food. It’s essential to differentiate between necessary nutrients found in natural foods and added sugars in processed foods, focusing on moderation.
Why is it important to differentiate between sugar and addictive substances?
Classifying sugar as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine can be counterproductive, as it may discourage enjoyment of the naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and vegetables. Understanding the nuances of sugar’s role helps promote healthier dietary choices.
What should I be aware of when reading food labels regarding sugar?
Check food labels for added sugars, particularly in processed snacks and beverages, to make informed decisions about your sugar intake. Being aware of hidden sugars can help manage cravings and maintain healthier consumption habits.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Nature of Sugar Addiction | Sugar increases cravings and can lead to compulsive eating, but it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Comparative Severity | Withdrawal symptoms from sugar are mild compared to those of addictive drugs, making sugar less severe in terms of addiction. |
| Presence in Diet | Sugar is a part of many essential foods, such as fruits and whole grains, which are necessary for survival. |
| Recommended Intake | The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Gradual Reduction Advice | Cutting sugar drastically can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms, so it is advisable to reduce intake gradually. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This is a complex question that elicits diverse opinions from health experts. While sugar does have some addictive qualities, it is not officially recognized as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The craving and consumption of sugar-laden processed foods can create habitual eating patterns, akin to some aspects of addiction, but the withdrawal symptoms are considerably milder. Understanding the appropriate consumption levels of sugar is critical for maintaining a healthy lifestyle without entirely eliminating this sweet substance from our diets.