Bile acid imbalance can play a critical role in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is the most prevalent form of liver malignancy. Recent research highlights how disturbances in bile acid metabolism can lead to serious liver conditions, driving a deeper investigation into potential liver cancer treatments. Bile acids, pivotal in fat digestion, have hormone-like properties that regulate various metabolic processes, creating a complex relationship with liver health. The study by Yingzi Yang and her team identifies a key molecular switch linked to the Hippo/YAP pathway, offering fresh insights into the underlying mechanisms of liver cancer. Understanding how YAP FXR signaling impacts bile acid levels may illuminate new pharmacological strategies for preventing and treating liver cancer.
The disruption of bile acid homeostasis is increasingly being recognized as a significant factor in liver malignancies, particularly in cases of hepatocellular carcinoma. Previous research has established that bile acids, crucial for fat digestion, also exert regulatory effects on metabolic pathways, showcasing their importance beyond mere digestion. In light of this, the key molecular pathways that influence bile acid production and their relationship to liver health become essential in understanding cancer progression. The interactions between YAP and FXR within the liver present a potential target for innovative treatments aimed at restoring balance in bile acid levels. These findings usher in a new era of liver cancer research, focusing on the metabolic implications of bile acids and their broader influence on hepatic health.
Understanding Bile Acid Imbalance and Its Link to Liver Cancer
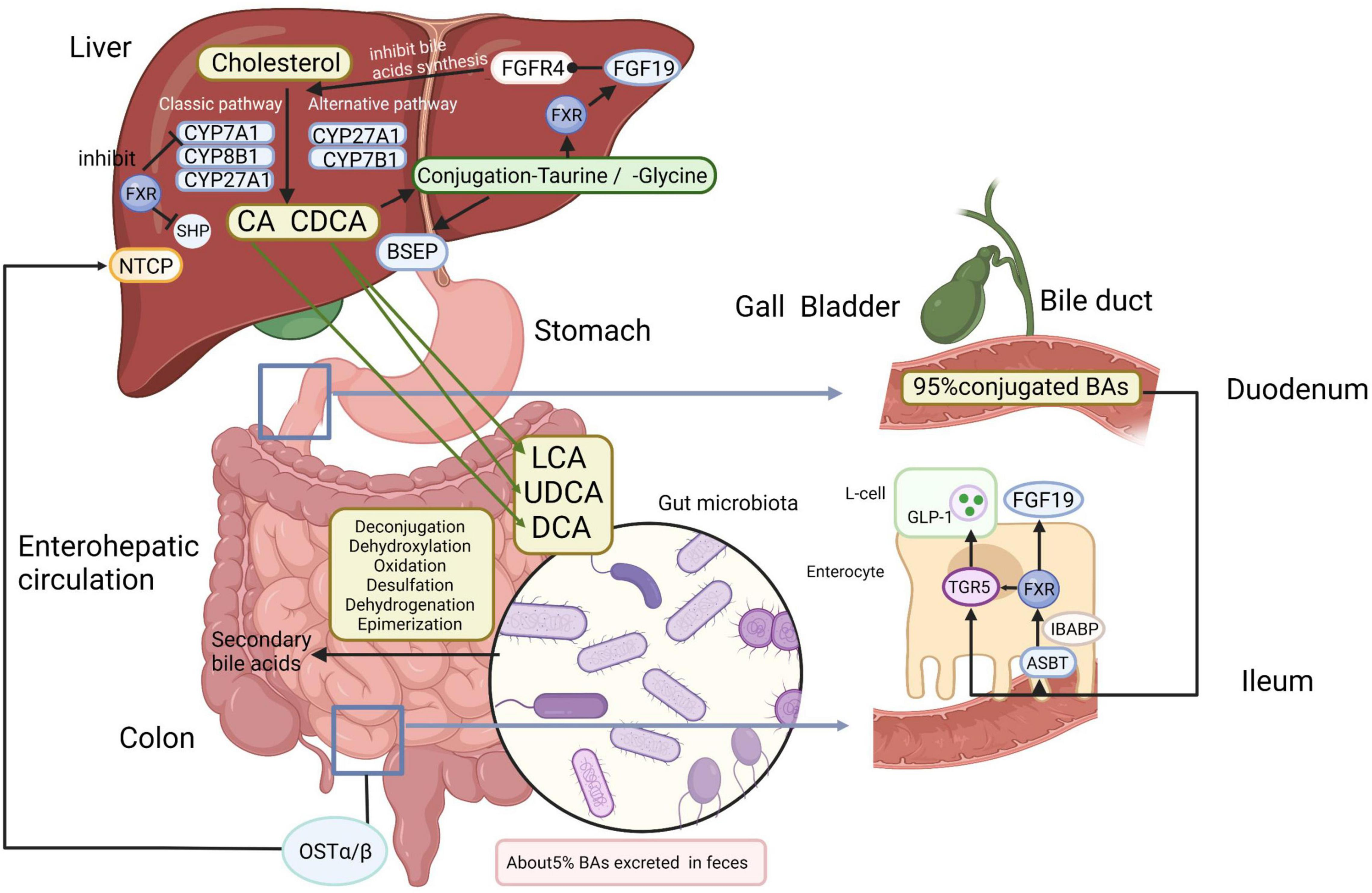
Bile acids are crucial components produced by the liver that aid in fat digestion and nutrient absorption. However, an imbalance in bile acid metabolism can cause liver injury and inflammation, directly contributing to the development of liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Research has shown that when bile acids accumulate excessively in the liver, they lead to toxic effects that can initiate a cascade of events, ultimately resulting in cancer. This link between bile acid imbalance and liver cancer underscores the importance of maintaining liver health through proper bile composition and metabolism.
Recent studies highlight the role of molecular pathways in regulating bile acid levels, particularly focusing on the YAP protein and its interaction with the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR). YAP, a significant player in cellular signaling and growth regulation, appears to adjust bile acid metabolism, promoting conditions conducive to liver cancer. By disrupting normal FXR function, YAP can cause an overproduction of bile acids, leading to liver fibrosis and eventually carcinogenic transformation in liver cells. Understanding these mechanisms opens new avenues for liver cancer treatment and prevention.
The Role of YAP and FXR Signaling in Liver Health
The YAP protein plays a pivotal role in cancer biology by influencing cellular processes such as growth and apoptosis, particularly in liver tissues. Research indicates that while YAP typically promotes cell proliferation, it can paradoxically act as a repressor in the context of bile acid signaling. This unique regulatory mechanism highlights how YAP’s activity disrupts the normal balance maintained by FXR, which is essential for bile acid homeostasis. By understanding the critical interplay between YAP and FXR, researchers can identify potential therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring this balance to prevent liver disease.
Enhancing FXR signaling could be a promising therapeutic strategy in mitigating liver cancer risk associated with bile acid imbalances. Treatments aimed at stimulating FXR activity can potentially reverse the harmful effects induced by YAP overactivity, such as fibrosis and inflammation. By employing pharmacological agents that enhance FXR signaling or encourage the excretion of excess bile acids from the liver, the damaging cycle that leads to hepatocellular carcinoma can be interrupted. This approach not only sheds light on liver cancer treatment but also emphasizes the critical need for comprehensive liver health maintenance.
Exploring Treatment Interventions for Liver Cancer
Current research into liver cancer treatments includes investigating various molecular pathways that can mitigate the effects of bile acid imbalances. One of the most promising avenues is the manipulation of FXR signaling, which can regulate bile metabolism effectively. Potential treatments could focus on pharmacological agents designed to enhance FXR activity, thereby restoring balance to bile acid levels and protecting the liver from damage. These interventions could be instrumental for patients presenting early signs of liver disease or those at high risk for developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
Moreover, the discovery of YAP as a repressive factor in bile acid metabolism opens up new therapeutic windows. By targeting the pathways associated with YAP and FXR, researchers can develop more sophisticated treatment strategies that not only address existing liver damage but also prevent future incidences of liver cancer. Continued exploration in this field could lead to innovative therapies that significantly improve outcomes for patients suffering from liver diseases.
The Importance of Bile Acids in Liver Function
Bile acids are not merely digestive detergents; they play a critical hormonal role in regulating various metabolic pathways essential for overall liver health. Produced in the liver and transported to the small intestine, bile acids facilitate fat absorption and support metabolic processes. They interact with nuclear receptors, like FXR, that maintain bile homeostasis, ensuring that appropriate levels are metabolized and excreted. Any disturbance in this finely-tuned system can lead to severe consequences, including liver fibrosis and cancer.
Maintaining an optimal bile acid profile is essential for preventing liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Factors such as diet, metabolite levels, and genetic predispositions can influence bile acid composition, potentially leading to imbalances that exacerbate liver conditions. Therefore, understanding the intricate role of bile acids within liver function will enhance approaches to liver health and disease management. This knowledge is critical for informing both clinical practices and public health strategies.
Lifestyle Changes for Preventing Bile Acid Imbalance
Preventing bile acid imbalance is essential to reduce the risk of liver diseases, including liver cancer. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a balanced diet rich in fiber, healthy fats, and adequate hydration, play a key role in promoting liver health. Foods high in antioxidants can help combat oxidative stress, while regular physical activity can enhance metabolic function, including bile acid metabolism. By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing conditions that may lead to hepatocellular carcinoma.
In addition to dietary changes, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and managing body weight are vital strategies for maintaining optimal liver function. Excessive alcohol intake can cause liver damage and disrupt bile acid production, leading to metabolic dysregulation. Likewise, maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of fatty liver disease, a precursor to liver cancer. Public health initiatives promoting awareness about liver health can assist communities in adopting preventive practices while encouraging research into the molecular links between diet, bile acids, and liver cancer.
Novel Research Directions in Liver Cancer Treatments
Recent studies focusing on the roles of bile acids and their signaling pathways in liver health have sparked new research directions aimed at developing targeted treatments for liver cancer. As scientists explore the mechanisms by which bile acid imbalances can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma, significant efforts are directed towards identifying specific molecular targets, such as the FXR pathway. These studies are crucial for innovating therapeutic strategies that harness the body’s natural bile metabolism to counteract cancer progression.
Furthermore, understanding the regulatory roles of various signaling pathways, including YAP and FXR interactions, could lead to breakthrough treatments that enhance liver cancer management. Researchers are investigating pharmacological compounds that can modulate these pathways, potentially offering new hope to patients diagnosed with liver cancer. These novel treatment directions not only address existing liver diseases but also contribute to the understanding of preventative measures that could be implemented long before the onset of severe complications.
The Impact of Bile Acid Deficiency on Liver Health
Bile acid deficiency can have a profound impact on liver health, often leading to the development of various liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. When bile acids are insufficient, the liver struggles to perform critical functions such as digestion and metabolism, resulting in the accumulation of toxins and harmful substances within the body. Such accumulation can trigger chronic inflammation and ultimately increase the risk of cancerous transformations in liver cells.
Furthermore, understanding the consequences of bile acid deficiencies highlights the importance of assessing bile acid levels in patients with liver disease. Early intervention through dietary modifications or supplementation could help restore balance, promote liver health, and prevent further complications, including cancer. As research continues to uncover the intricacies of bile acid metabolism, its role in liver disease—including the potential progression to HCC—remains a focal point in the quest for effective treatment solutions.
Integrating Molecular Research with Clinical Practices for Liver Cancer
The intersection of molecular research and clinical practice is critical in advancing our understanding of liver cancer treatment strategies. Discoveries regarding the role of bile acids, YAP signaling, and FXR activation pave the way for integrating scientific findings into therapeutic applications. By bridging the gap between laboratory research and patient care, healthcare professionals can enhance the precision of liver cancer treatments based on individual molecular profiles.
Moreover, ongoing research efforts will continue to expand our understanding of how bile acid metabolism can inform clinical decision-making. Physicians may utilize molecular insights to develop personalized treatment plans that consider each patient’s unique liver health status and metabolic profiles. This integrative approach not only optimizes treatment outcomes but also improves the quality of care for patients battling liver cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the link between bile acid imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile acid imbalance is linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), as it can lead to liver injury and chronic inflammation. Disruptions in bile acid homeostasis can promote tumor formation through mechanisms involving the YAP signaling pathway, which interferes with the function of the FXR receptor that regulates bile acids.
How does YAP FXR signaling affect liver cancer development?
YAP FXR signaling plays a critical role in liver cancer development. When YAP is activated, it represses the FXR receptor, which is essential for maintaining bile acid balance. This can result in overproduction of bile acids, leading to liver damage, fibrosis, and ultimately, hepatocellular carcinoma.
What are the potential treatments for bile acid imbalance related to liver cancer?
Potential treatments for bile acid imbalance related to liver cancer may involve enhancing FXR function to restore bile homeostasis or promoting bile acid excretion. Research suggests that pharmacological solutions stimulating FXR could reduce liver damage and cancer progression.
Can liver cancer treatment strategies target bile acid metabolism?
Yes, liver cancer treatment strategies can target bile acid metabolism. By understanding the mechanisms of bile acid imbalance and the role of YAP and FXR signaling, new therapeutic approaches can be developed to prevent liver cancer by correcting bile acid dysregulation.
What role do bile acids play in liver health?
Bile acids are crucial for liver health as they aid in fat digestion and absorption. They also function in a hormone-like capacity, regulating metabolic processes. An imbalance in bile acids can lead to liver diseases, including inflammation and cancer, highlighting their importance in maintaining overall liver function.
What are the implications of the recent findings on bile acid imbalance and liver cancer?
The recent findings indicate a significant connection between bile acid imbalance and liver cancer, particularly through the YAP FXR signaling pathway. This knowledge could lead to innovative treatment options and better prevention strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma by focusing on bile acid regulation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Acid Imbalance | A disruption in bile acid production can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The imbalance is linked to liver injury and inflammation. |
| Key Molecular Switch | The study identified a molecular switch that regulates bile acids, providing new insights for potential liver cancer treatments. |
| YAP and FXR Relationship | YAP traditionally promotes cell growth but acts as a repressor in bile acid metabolism by inhibiting FXR, leading to bile acid overproduction. |
| Potential Treatment Approaches | Research suggests enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion can reduce liver damage and prevent cancer progression. |
Summary
Bile acid imbalance liver cancer is increasingly recognized as a crucial area of research linking liver health and cancer development. A recent study has unveiled how disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By identifying the relationship between YAP and FXR in bile metabolism, this research sheds light on potential therapeutic interventions. Enhancing FXR functionality may present a promising approach to mitigate liver damage and halt cancer progression.