Emerging research has unveiled a significant connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer, particularly highlighting its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This form of liver cancer arises from unhealthy bile acid levels affecting liver function and overall metabolism. When the regulatory mechanisms of bile acids are disrupted, it can lead to severe liver injury, inflammation, and ultimately, cancerous growths. Insights into the FXR receptor’s function have shed light on potential liver cancer treatments, revealing that by managing bile acid levels, we may influence cancer progression. Additionally, the role of the YAP protein in this mechanism opens new avenues for therapeutic interventions that target bile acids to prevent or treat liver malignancies.
Recent studies have identified a critical link between dysregulated bile acids and liver malignancies, particularly focusing on the dynamics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, essential for fat digestion and metabolic regulation, can become harmful when their balance is disrupted. Researchers have turned their attention to molecular players such as the FXR receptor and the YAP protein, which play pivotal roles in maintaining bile acid homeostasis and regulating liver health. Understanding these interactions offers promising insights into innovative liver cancer treatment strategies. By exploring various regulatory pathways, scientists aim to find effective methods to restore bile balance, potentially halting the progression of liver cancer.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Connection to Liver Cancer
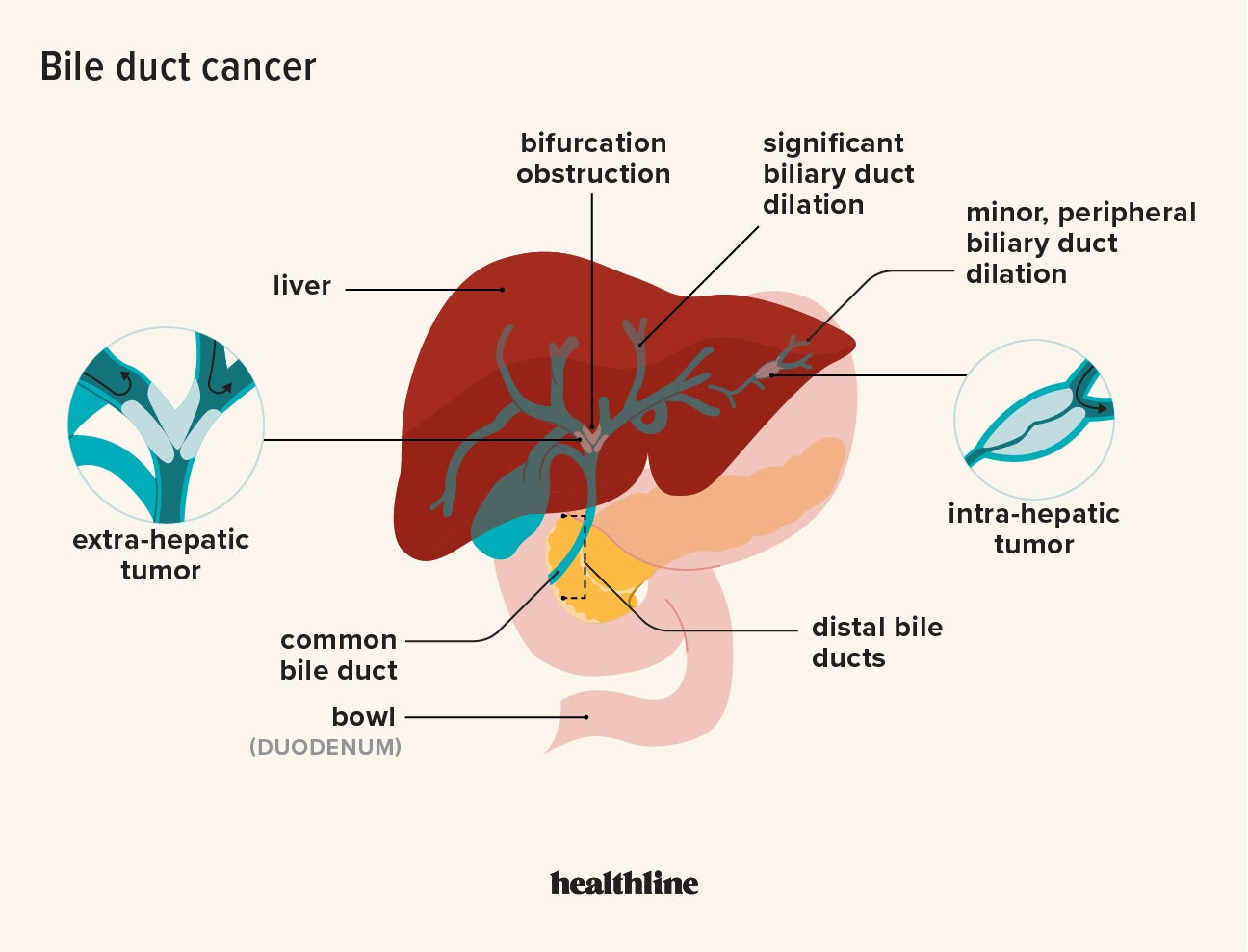
Bile imbalance can significantly disrupt liver functions and is linked to various liver diseases, notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver’s ability to produce bile is essential for fat digestion, but when the balance of bile acids is disturbed, it can trigger a cascade of negative health effects, including liver injury and inflammation. Such disruptions have been shown to lead to the development of HCC, the most prevalent form of liver cancer, making understanding this condition imperative for effective liver cancer treatment.
Recent research highlights a crucial molecular switch that regulations bile acid metabolism. Scientists have identified the role of YAP protein, which, contrary to promoting growth, represses vital functions of the FXR receptor, a significant bile acid sensor. This inhibition causes an overproduction of bile acids, leading to systemic fibrosis and inflammation, both precursors to cancer. Addressing this bile imbalance could pave the way for new therapeutic strategies in battling liver cancer.
The Role of FXR Receptor in Regulating Bile Acids
The FXR (Farnesoid X Receptor) is a nuclear receptor critical for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. FXR regulates bile acid synthesis and transport, ensuring a balanced cycle of production and excretion. When FXR function is compromised, usually due to factors like YAP activation, bile acids become dysregulated, resulting in toxic accumulation within the liver. This imbalance not only aggravates liver conditions but also increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
Strategies that enhance FXR function could help in restoring normal bile acid levels, thereby reducing liver damage and the risk of liver cancer. Promoting FXR activity can lead to improved metabolic control and reduced bile acid toxicity, thus mitigating the adverse effects associated with bile imbalance. This points to the potential of pharmacological interventions targeting FXR as a promising approach for liver cancer treatment.
The Impact of YAP Protein on Cancer Development
YAP (Yes-associated protein) plays a complex and paradoxical role in cancer. While it is traditionally understood to promote tumor growth, recent findings reveal its involvement in the repression of bile acid metabolism via FXR disruption. This surprising function indicates that YAP does not merely drive cell proliferation but can also exacerbate conditions like liver cancer through altered bile acid regulation, leading to increasing liver fibrosis and inflammation.
Inhibiting YAP’s repressive actions on FXR presents a novel therapeutic angle. By blocking YAP, researchers believe that normal bile acid metabolism can be restored, potentially halting the progression of liver damage and inhibiting the development of HCC. This shift in understanding underscores the need for comprehensive approaches in liver cancer research, focusing not just on growth promotion but also on the metabolic pathways influenced by proteins like YAP.
Molecular Mechanisms Behind Bile Acid Metabolism
Bile acids function not only in digestion but are also vital signaling molecules that regulate numerous metabolic processes. The liver’s regulation of bile acids involves intricate molecular mechanisms, with FXR playing a pivotal role. When bile acids bind to FXR, they promote processes such as bile acid synthesis, excretion, and the overall maintenance of metabolic homeostasis. Disruption of this balance, particularly through YAP activity, can trigger a detrimental cycle that leads to liver inflammation and cancer.
Understanding these molecular underpinnings sheds light on potential therapeutic interventions in liver cancer treatment. Enhancing FXR’s effectiveness, employing compounds that inhibit YAP, or promoting the expression of bile acid export proteins could help restore normal bile acid levels, thus reducing the risk of disease progression. The interplay between these molecular players is critical for developing targeted treatments for conditions linked to bile imbalance.
The Potential for Pharmacological Innovations in Liver Cancer Treatment
The recent discoveries regarding bile acid metabolism and its links to liver cancer open doors for innovative pharmacological treatments. By targeting the FXR receptor and exploring compounds that can enhance its function, researchers can address the core issues stemming from bile acid imbalance. This therapeutic avenue could lead to significant reductions in liver damage and slower progression of diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma.
Moreover, understanding the repressive role of YAP on bile acids offers additional opportunities for pharmacological intervention. By creating drugs that inhibit YAP or adjust its activity, it is possible to restore proper bile acid homeostasis and, in turn, mitigate the risk of cancer development. The actionable insights gained from recent studies signify a promising horizon in liver cancer treatment, focusing on the interconnectedness of bile acids, metabolic regulation, and cancer progression.
Role of Bile Acids in Metabolic Regulation
Bile acids play an essential role in metabolic regulation beyond their primary function in fat digestion. They influence various pathways that govern energy homeostasis, glucose metabolism, and even inflammation. This multifunctional aspect of bile acids indicates their importance in liver health, where their imbalance may lead to metabolic disorders and diseases including HCC. The detailed study of bile acid signaling mechanisms is crucial for understanding their broader implications on health and disease.
Recent research shows that disturbances in bile acid metabolism, particularly through disruptions involving the FXR receptor and the YAP protein, have profound effects on metabolic regulation. Therefore, optimizing bile acid profiles could serve as a therapeutic target for metabolic diseases and liver-related conditions. By restoring proper bile acid function, new strategies may emerge to combat liver cancer and improve metabolic outcomes.
Understanding Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Causes and Consequences
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents a significant global health challenge, often arising from underlying liver diseases such as cirrhosis or chronic inflammation linked to bile imbalance. Factors that contribute to the onset of HCC include lifestyle choices, viral hepatitis infections, and metabolic syndromes, highlighting the complex interplay of various risk factors. Additionally, the role of bile acid dysregulation, influenced by proteins like YAP and FXR, is increasingly being recognized as a pivotal contributor to HCC development.
Addressing the causes of HCC involves not only targeting established risk factors but also outright managing the biochemical imbalances in bile acids that can prematurely push the liver towards cancer. By increasing awareness of these mechanisms, it is possible to implement preventive measures and develop therapies that reduce the incidence of liver cancer related not just to direct toxicities but also to metabolic dysfunction.
New Horizons in Cell Signaling and Liver Health
Cell signaling plays a foundational role in maintaining liver health and preventing disease. Understanding how pathways like Hippo/YAP influence liver cell growth and bile acid metabolism is critical in deciphering mechanisms of liver diseases, particularly those that culminate in cancer. The interplay between cell signaling, lipid metabolism, and inflammation frames a comprehensive picture of the liver’s role in systemic health.
Research into these biological pathways not only furthers our understanding of liver cancer but also highlights potential biomarkers for early detection and targets for intervention. As advancements are made in molecular science, there lies the promise of innovative diagnostic and therapeutic tools that will enable more effective management of liver disease and potentially save countless lives.
Strategies for Improving Bile Acid Excretion
Improving bile acid excretion is a promising strategy for mitigating liver damage and reducing cancer risk. Current research emphasizes the importance of transport proteins like BSEP (bile salt export pump), which play a critical role in bile acid secretion from the liver to the intestine. Enhancing the expression and function of such transporters could directly alleviate the harmful accumulation of bile acids, thus counteracting inflammation and oxidative stress in liver tissues.
Moreover, lifestyle modifications, dietary interventions, and pharmaceutical advances aimed at promoting bile acid excretion could serve as adjunct therapies in preventing conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma. Furthermore, understanding how signaling pathways affect bile acid transport can lead to novel therapeutic targets that can effectively prevent the transition from bile imbalance to cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance is closely linked to liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Research indicates that disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are risk factors for liver cancer. The overproduction of bile acids caused by dysregulation can promote tumor growth and progression.
How does bile acid function contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma development?
Bile acids serve important roles in fat digestion and regulation of metabolic processes. When bile acid production is imbalanced, particularly through the action of the YAP protein affecting the FXR receptor, this can lead to increased bile acid accumulation in the liver, resulting in conditions that may promote hepatocellular carcinoma.
What role does the FXR receptor play in liver cancer and bile acid homeostasis?
The FXR receptor (Farnesoid X Receptor) is crucial for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. It regulates bile acid metabolism, preventing excessive bile acid accumulation. When the FXR receptor is paralyzed by the YAP protein, it disrupts this balance, potentially leading to liver fibrosis and increasing the risk of liver cancer.
Can liver cancer treatment be influenced by understanding bile acid metabolism?
Yes, liver cancer treatment may benefit from insights into bile acid metabolism. By targeting the pathways involving YAP and FXR, researchers are exploring pharmacological strategies to enhance FXR function or promote bile acid excretion, which could mitigate liver damage and slow cancer progression.
What is the significance of the Hippo/YAP pathway in liver cancer and bile imbalances?
The Hippo/YAP pathway is significant in liver cancer as it regulates cell growth and impacts bile acid metabolism. The activation of YAP can repress FXR function, leading to bile acid dysregulation and subsequent liver inflammation and cancer. Targeting this pathway presents a potential therapeutic approach in managing liver cancer risks.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | Critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common liver cancer. |
| Role of Bile | Bile aids in fat digestion and has hormone-like roles affecting metabolic processes. |
| Molecular Findings | Identification of a key molecular switch (YAP) that impacts bile acid metabolism and promotes tumor formation. |
| YAP and FXR Relationship | YAP interferes with FXR, disrupting bile acid homeostasis, leading to liver damage and potentially cancer. |
| Potential Interventions | Blocking YAP activity or enhancing FXR function may prevent liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Applications of Findings | Study results could lead to new pharmacological treatments that stimulate FXR. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a pressing concern as recent studies have shown that disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma, the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that underlie bile acid metabolism, particularly the roles of YAP and FXR, illuminates potential pathways for new treatment strategies. By addressing the imbalance through enhanced FXR function or targeted pharmacological interventions, we may develop effective solutions to combat liver cancer linked to bile imbalance.