CALEC surgery, also known as cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell therapy, is revolutionizing the treatment of corneal injuries that were once considered incurable. Developed by a team at Mass Eye and Ear, this innovative procedure employs stem cell therapy to regenerate the cornea’s surface, offering new hope to patients suffering from severe vision impairments. By transplanting limbal epithelial cells harvested from a healthy eye into a damaged one, CALEC surgery has demonstrated remarkable success rates, with over 90 percent of participants experiencing effective cornea restoration. This advancement in eye repair methods not only showcases the potential of stem cell applications in ophthalmology but also opens new avenues in cornea restoration research. Empowering patients to regain their sight, CALEC surgery is setting a new standard in the treatment of devastating corneal injuries.
The field of ocular regenerative medicine has taken a giant leap forward with the introduction of cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell therapy, commonly referred to as CALEC surgery. This pioneering method leverages the regenerative power of stem cells to address serious injuries to the cornea, which are often resistant to traditional treatment approaches. By creating a graft from the patient’s own healthy limbal epithelial cells, practitioners can effectively restore the corneal surface, significantly improving visual outcomes. As researchers delve deeper into advanced eye repair techniques, this groundbreaking procedure not only highlights the effectiveness of stem cell applications but also emphasizes the importance of cornea restoration in improving patients’ quality of life. The exploration of CALEC surgery marks an exciting era in the treatment of ocular pathologies, redefining hope for those affected by corneal damage.
Understanding CALEC Surgery: A New Approach to Eye Repair
The CALEC surgery, or cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells transplantation, represents a breakthrough in corneal damage treatment. This innovative technique is primarily focused on patients suffering from limbal stem cell deficiency due to diverse causes such as corneal injuries or chemical burns. Prior to this procedure, many of these injuries were deemed untreatable, leaving patients with limited options and ongoing visual impairment. CALEC surgery utilizes stem cells derived from a healthy eye to create a graft that can regenerate the cornea’s surface, providing hope for those who had been previously told there were no effective treatments available.
The effectiveness of CALEC surgery has been demonstrated in clinical trials, where over 90% of treated patients showed significant improvement in cornea restoration. This method not only restores vision but also alleviates pain associated with corneal injuries. Through a meticulous process, the surgeon harvests limbal epithelial cells from the patient’s healthy eye, cultivates them in a controlled environment, and then implants the rejuvenated tissue into the damaged eye. This process highlights the synergistic combination of cutting-edge cell manufacturing techniques and surgical intervention.
The Role of Stem Cell Therapy in Corneal Injuries Treatment
Stem cell therapy is at the forefront of modern medical advancements, especially in the realm of ophthalmology. For corneal injuries, where traditional repair methods may fall short, stem cells present a revolutionary way to regenerate damaged tissues. The application of cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells in CALEC surgery exemplifies how stem cell therapy can transform the treatment landscape for patients facing debilitating eye conditions. By harnessing the body’s own resources, this approach significantly reduces the risk of rejection and complications that often accompany traditional transplantations.
The outcomes of stem cell therapy in treating corneal injuries have been promising. Clinical trials have shown that patients who underwent CALEC surgery not only regained their corneal integrity but also experienced marked improvements in their visual acuity. This approach addresses the underlying issue of limbal stem cell deficiency head-on, re-establishing the cornea’s health rather than merely masking symptoms. As researchers continue to explore the potentials of stem cell applications in ophthalmology, the journey towards widespread acceptance and approval of such therapies is gaining momentum.
Innovative Eye Repair Methods: Shaping the Future of Ophthalmology
Innovative eye repair methods like CALEC surgery stand as a testament to how far ophthalmology has progressed in treating severe eye conditions. The traditional methods focused primarily on managing symptoms or relying on corneal transplants, which were not always viable for patients with inadequate donor tissue or multiple corneal injuries. With the advent of regenerative medicine, techniques such as CALEC surgery aim to address the root causes of corneal damage, restoring the eye’s natural function more effectively.
The future of eye repair methods, particularly through stem cell therapies, looks promising. Researchers are optimistic that further studies and clinical trials will lead to improved practices and broader applicability. As techniques are refined and more data becomes available concerning their efficacy and safety, it’s likely that we will see these methods become standard treatments. Ultimately, the goal is to enable all patients with corneal damage, irrespective of the severity of their condition, to access advanced therapeutic options that promote healing and improved quality of life.
Limbal Epithelial Cells: The Key to Corneal Restoration
Limbal epithelial cells play a crucial role in maintaining the clarity and health of the cornea. These cells, found at the cornea’s border, are essential for replenishing damaged epithelial layers and ensuring the cornea’s overall integrity. When the cornea is injured through trauma or illness, the depletion of these cells can lead to lasting damage and significant vision loss. The CALEC surgery offers a targeted solution by utilizing these vital cells to facilitate regeneration and restore the corneal surface.
Research into limbal epithelial cells has opened new avenues in cornea restoration. By isolating and culturing these cells, medical professionals can create grafts capable of repairing even the most compromised corneas. The application of these cells in CALEC surgery not only highlights their importance but also reflects the growing understanding and potential of regenerative medicine in ophthalmology. As investigations continue, further advancements are expected to follow, potentially expanding the pool of patients who can benefit from stem cell-based treatments.
Research Progress in Cornea Restoration: A Collaborative Effort
Ongoing research and collaboration have been pivotal in advancing cornea restoration techniques like CALEC surgery. The partnership between institutions such as Mass Eye and Ear and specialized labs has led to the successful development and implementation of this groundbreaking approach. Collaborative efforts in research not only enhance clinical understanding but also promote faster translation of laboratory findings into practical treatments. For instance, the initial studies that laid the groundwork for CALEC surgeries drew on insights from various dedicated teams, each contributing their expertise to overcome critical challenges.
Moreover, ongoing studies emphasize the importance of community and academic partnerships in enhancing patient care and treatment outcomes. By pooling resources and knowledge, researchers aim to refine procedures, extend the benefits of CALEC surgeries to a broader patient population, and ensure the highest standards of safety and efficacy. This collaborative spirit is crucial, as future trials will likely require more extensive participation and a well-structured protocol to thoroughly assess long-term outcomes.
Patient Outcomes: Evaluating the Success of CALEC Surgery
Evaluating the success of CALEC surgery involves monitoring patient outcomes over time, particularly regarding corneal restoration and vision improvement. In clinical trials, significant percentages of participants showed complete restoration of the corneal surface and enhanced visual acuity within 12 to 18 months of surgery. These positive outcomes underscore the treatment’s promise for individuals who have suffered from debilitating corneal injuries and were previously considered untreatable.
Despite the overwhelmingly positive results, researchers have noted the need for additional scrutiny to ensure that CALEC surgery can be effectively replicated across diverse patient populations. Collaboration in future trials will yield a more comprehensive understanding of both the short- and long-term effects of the treatment, improving protocol and patient care methods. This ongoing evaluation is essential in moving closer to an optimal model for treating corneal injuries with stem cell therapy.
Safety Profile of CALEC Surgery: What Patients Should Know
Safety is a primary concern for patients considering experimental procedures like CALEC surgery. Early trials have shown a strong safety profile, with no serious adverse events reported among patients who underwent the procedure. Minor complications were resolvable, demonstrating that while there are inherent risks in surgical interventions, CALEC surgery has managed to minimize significant health threats. This encouraging safety record is vital in building trust among patients and practitioners alike.
Prospective candidates for CALEC surgery should discuss thoroughly with their healthcare providers about the safety measures and monitoring in place during the trial. Moreover, understanding the nature of minor adverse events and their resolution can provide further reassurance. As further research is conducted, ongoing safety assessments will continue to refine the protocol and enhance the efficacy of CALEC surgery, aiming to establish it as a viable treatment option in everyday clinical practice.
Future Perspectives in Cornea Restoration Research
The future of cornea restoration research is undeniably bright as techniques like CALEC surgery advance. Researchers are enthusiastic about the possibility of expanding the application of limbal stem cells, delving into allogeneic grafts and potential applications for patients with bilateral corneal injuries. These developments could significantly broaden the demographic reach of the treatment, providing new hope to those who currently have limited options for vision rehabilitation.
Continued investment in this field of research is crucial to overcome existing limitations. Future studies may involve larger patient cohorts and use advanced randomized-controlled designs to gather robust data on the long-term safety and efficacy of CALEC surgery. With a commitment to enhancing knowledge and practice in stem cell therapy, the path toward FDA approval and widespread availability of CALEC surgery looks promising, providing potentially life-changing outcomes for many.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CALEC surgery and how does it relate to stem cell therapy?
CALEC surgery, or cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell surgery, is an innovative procedure that uses stem cell therapy to treat blinding corneal injuries. This technique involves harvesting stem cells from a healthy eye, cultivating them into a graft, and then transplanting this graft into the damaged eye, effectively restoring the cornea’s surface.
How effective is CALEC surgery in the treatment of corneal injuries?
Research has shown that CALEC surgery has over 90 percent effectiveness in restoring the surface of the cornea. Clinical trials reported complete corneal restoration in 50 percent of participants after three months, with success rates reaching 93 percent at 12 months, demonstrating its promise in treating severe corneal injuries.
What role do limbal epithelial cells play in cornea restoration research?
Limbal epithelial cells are crucial for maintaining the cornea’s smooth surface. In cases of corneal injuries where these cells are depleted, CALEC surgery aims to regenerate these cells using stem cell therapy, facilitating the restoration of the eye’s health and improving vision for patients.
Are there any risks associated with CALEC surgery?
CALEC surgery has demonstrated a strong safety profile, with no serious adverse events reported in the clinical trials. Minor complications, such as a bacterial infection in one participant, have occurred but were quickly resolved. Ongoing research aims to further assess the long-term safety of this eye repair method.
Why is CALEC surgery considered a breakthrough in eye repair methods?
CALEC surgery represents a significant advancement in eye repair methods, particularly for patients with corneal injuries previously deemed untreatable. This approach utilizes stem cell therapy to restore corneal health, offering new hope for individuals suffering from severe ocular damage.
What is the current status of CALEC surgery and its availability?
Currently, CALEC surgery is experimental and not widely available at any U.S. hospitals. Future studies are planned to broaden patient access and gather more data, which could lead to FDA approval for this innovative stem cell treatment for corneal injuries.
How long does it take to prepare for CALEC surgery after stem cells are harvested?
The process of creating a cellular tissue graft for CALEC surgery typically takes two to three weeks after harvesting stem cells from a healthy eye. This time is necessary to cultivate the limbal epithelial cells into a suitable graft for transplantation.
What future developments are anticipated in CALEC surgery and cornea restoration?
Future developments in CALEC surgery may include establishing a method for allogeneic grafts, allowing donors’ limbal stem cells to be used. This could potentially expand the availability of this treatment to individuals with corneal injuries affecting both eyes.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
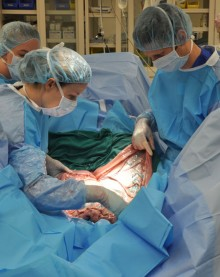
| First CALEC Surgery | Performed by Ula Jurkunas at Mass Eye and Ear. Photo courtesy of MGH Health. |
| Clinical Trial Results | The trial involved 14 patients, showing over 90% effectiveness in restoring the cornea’s surface. |
| Procedure Description | Involves stem cell extraction from a healthy eye, expansion into a graft, and transplantation. |
| Potential for Expansion | Future hopes for allogeneic stem cell sourcing for widespread application of CALEC. |
| Safety Profile | Strong safety profile with minimal adverse events reported during the trial. |
| Next Steps | Further studies needed for federal approval and larger patient groups. |
Summary
CALEC surgery represents a groundbreaking advancement in ophthalmic treatment by utilizing stem cell therapy to repair previously untreatable corneal damage. The success of the initial trials indicates a promising future for patients suffering from significant injury, with further studies essential for expanding the accessibility of this innovative treatment. As research continues to unfold, CALEC surgery could become a standard solution for restoring vision and improving quality of life for countless individuals.