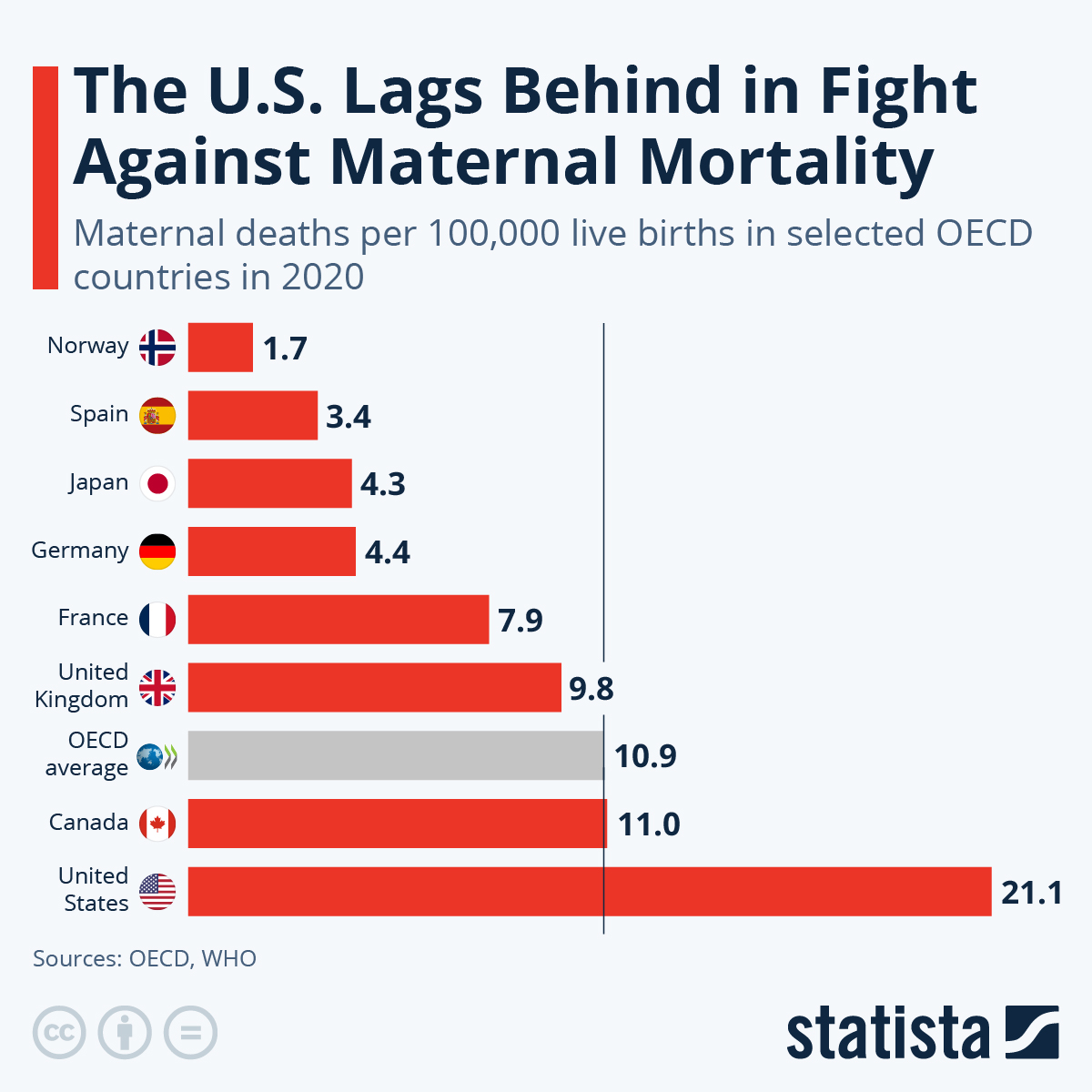
Maternal mortality rates are a pressing concern in the United States, revealing a troubling trend of rising pregnancy-related deaths over recent years. Compared to other high-income countries, the U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate, a statistic that underscores significant maternal health disparities. A new study indicates that over 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, yet systemic issues in U.S. pregnancy care continue to hinder progress. The sharp increases in mortalities, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, illuminate the urgent need for better prenatal care and comprehensive postpartum support to address preventable maternal deaths. This situation demands immediate attention as it not only affects the health of new mothers but also the well-being of families and communities alike.
When discussing maternal mortality, alternative terms such as pregnancy-related fatalities or maternal health challenges may come into play. This critical issue encompasses a variety of factors leading to the loss of life during or after pregnancy. The alarming trends in postpartum maternal deaths raise questions about the effectiveness of current healthcare policies and the accessibility of quality care. Addressing these complications calls for a deep dive into the systemic barriers faced by diverse racial and ethnic groups, as evidenced by the stark disparities in outcomes. By exploring the various dimensions of maternal health, we can begin to craft solutions to reduce preventable fatalities and enhance the overall well-being of mothers across the nation.
Understanding the Surge in U.S. Maternal Mortality Rates
The rise in maternal mortality rates in the United States has become a pressing public health concern. As noted in recent studies, the U.S. leads all high-income countries in maternal mortality, highlighting significant deficiencies within our healthcare infrastructure. This alarming trend underscores the need for improved prenatal care strategies and a more equitable delivery of services to pregnant individuals, particularly amid the evolving challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Experts point out that over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, making it imperative for policymakers to implement effective interventions.
Research has shown that maternal health disparities exist not just on a national scale but also at the state and local levels. Factors contributing to these disparities include socioeconomic status, geographic locations, and systemic racism within healthcare. The rise in maternal mortality rates among minority populations, such as American Indian, Alaska Native, and Black women, exemplifies the urgent need for targeted healthcare initiatives that address these inequities. By examining the intersections of race, health policy, and access to care, we can begin to formulate more effective solutions that can deliver better outcomes for all pregnant individuals in the U.S.
The Role of Health Disparities in Maternal Mortality
Maternal health disparities are a critical factor in the discussion surrounding pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. These disparities are often profound, with Black and Indigenous women facing disproportionately high mortality rates. Compounding these statistics are the socioeconomic barriers that many face, including lack of access to quality healthcare, nutrition, and education. Addressing these disparities is essential; research highlights that if maternal mortality rates in states with lower rates matched those of better-performing states like California, thousands of deaths could potentially be prevented each year.
Furthermore, systemic bias and discrimination intersect with income levels to exacerbate health disparities. It is clear that healthcare systems in many parts of the U.S. are not equipped to meet the diverse needs of pregnant women, which contributes significantly to higher rates of preventable maternal deaths. Initiatives aimed at combating these disparities must include comprehensive education for healthcare professionals to address implicit biases and to ensure equitable treatment across all racial and ethnic groups. Through concerted efforts, we can achieve a more equitable healthcare system that reduces the risk of maternal mortality.
The Importance of Extended Postpartum Care
Extended postpartum care is a critical yet often overlooked component of maternal health that requires immediate attention. Studies reveal that a substantial number of maternal deaths occur not only during pregnancy but also in the postpartum period, highlighting the need for a continuous care approach that extends beyond the traditional six-week check-up. Late maternal deaths, which occur between 42 days and a year post-delivery, must be incorporated into national discussions surrounding maternal health to provide a comprehensive view of the challenges women face after giving birth.
Enhanced postpartum care can significantly impact maternal mortality rates, especially when it encompasses mental health support, chronic condition management, and ongoing monitoring of physical health. Healthcare systems should aim to offer personalized care plans that address the unique needs of each mother during the recovery period. Investing in postpartum care isn’t just about preventing death; it’s about supporting women’s overall health and well-being, which is crucial for fostering healthy families and communities.
Addressing Preventable Maternal Deaths
Preventable maternal deaths remain a critical focus for public health campaigns. Research indicates that a staggering majority of pregnancy-related fatalities are preventable with the right support systems in place. This includes access to quality prenatal and postpartum care, education, and resources to address medical conditions that affect maternal health. Given the rise in such deaths in recent years, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, it becomes essential to reassess existing health policies and ensure that preventative measures are effectively integrated into all stages of maternal care.
Moreover, addressing preventable maternal deaths requires a multi-faceted approach that includes community engagement, healthcare provider training, and widespread awareness efforts. By promoting preventative health strategies, such as managing underlying medical conditions like hypertension and diabetes, we can substantially lower maternal mortality rates. Creating a healthcare environment that prioritizes proactive care over reactive treatment is essential for achieving meaningful reductions in maternal deaths.
Impacts of COVID-19 on Maternal Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly disrupted healthcare systems worldwide, including maternal healthcare in the U.S. The early phases of the pandemic revealed alarming spikes in maternal mortality rates, particularly in 2021. Interruptions to routine prenatal care, combined with increased stress and health risks associated with the virus, led to heightened concerns surrounding pregnancy-related deaths. The pandemic not only magnified existing disparities but also made clear the critical need for resilient healthcare systems that can withstand such crises.
As we navigate the ongoing effects of the pandemic, it is crucial to implement lessons learned about maternal health. Enhanced telehealth services, increased flexibility in care delivery, and stronger support networks are essential in ensuring that pregnant individuals receive the necessary care they need. The pandemic presents an opportunity to reevaluate maternal healthcare policies and solidify long-term strategies to improve outcomes, particularly for those most impacted by systemic challenges.
Combating Racial Inequities in Maternal Health
Combating racial inequities in maternal health is essential for improving overall maternal mortality rates in the U.S. Disparities experienced by racial and ethnic minorities, particularly Black and Indigenous women, are unacceptable. This ongoing issue reflects deep-seated systemic issues within healthcare that need urgent attention. By prioritizing strategies that target these inequities, such as increasing access to care, enhancing provider training on racial biases, and community outreach programs, we can pave the way for a more equitable maternal healthcare system.
Moreover, initiatives aimed at ensuring that diverse voices are represented in research and policy-making are critical for developing effective solutions tailored to the needs of marginalized communities. Listening to the experiences of those directly affected by maternal health disparities can lead to more informed policies and practices that foster trust within healthcare. Achieving equity in maternal health not only requires policy changes but a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation by healthcare systems.
Innovative Solutions in Maternal Healthcare
Innovative solutions in maternal healthcare are key to addressing the growing rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. As healthcare providers and policymakers strive to reduce pregnancy-related deaths, the integration of technology, enhanced healthcare access, and holistic health services play pivotal roles. Telemedicine, for example, has emerged as a vital tool for facilitating better access to care for pregnant individuals, especially during remote or underserved situations. This digital transformation can help bridge gaps in healthcare delivery that have been evident during the pandemic.
Seeking out innovative strategies also entails investing in research focused on maternal health, particularly in understanding the impacts of chronic diseases and mental health conditions on pregnancy outcomes. Adaptive approaches that consider cultural and social influences surrounding maternal care can lead to more effective interventions designed for specific populations. By fostering innovative solutions and leveraging technology, we can create a robust support system that greatly enhances maternal health outcomes.
Fostering Education on Maternal Health
Education plays a crucial role in addressing maternal mortality rates and combating health disparities. Raising awareness about the risk factors associated with pregnancy-related deaths, as well as empowering women through informed decision-making, can lead to significant health improvements. Comprehensive educational programs should aim to reach not only healthcare providers but also expectant mothers and their families, providing them with essential knowledge about prenatal care, managing chronic conditions, and recognizing the signs of potential complications.
Additionally, maternal health education should incorporate culturally relevant information tailored to the diverse populations in the U.S. By promoting health literacy, we empower individuals to advocate for themselves and seek care when necessary, reducing the risk of preventable maternal deaths. Strategies to enhance education should also include community workshops, support groups, and resource networks that foster open discussions about maternal health challenges, ultimately contributing to a more informed and supportive environment for pregnant individuals.
The Future of Maternal Healthcare in the U.S.
Looking toward the future, maternal healthcare in the U.S. must prioritize integrated care systems that are responsive to the complex needs of mothers and their families. This includes not only ensuring that healthcare providers have access to accurate information about risks associated with maternal mortality but also advocating for policies that support equitable access to care for all women. The emphasis should be placed on the continuum of care that encompasses prenatal, maternal, and postpartum services, creating seamless transitions that prioritize the health of mothers.
Furthermore, improving maternal health outcomes will require a collective effort from various stakeholders, including healthcare systems, public health organizations, policymakers, and communities. Together, they can implement strategies that address the root causes of maternal health disparities, ensuring that every woman has the opportunity to experience a safe and healthy pregnancy. By fostering collaboration and innovation, we can envision a future where maternal mortality rates are significantly reduced and maternal health is genuinely prioritized.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of increasing maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
The increasing maternal mortality rates in the U.S. are attributed to several factors, including a fragmented healthcare system, systemic inequities, and rising chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease among reproductive-age individuals. Improving prenatal and postpartum care is essential to address these issues effectively.
How do maternal health disparities affect pregnancy-related deaths across different demographics?
Maternal health disparities significantly impact pregnancy-related deaths, particularly among racial and ethnic groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience mortality rates nearly four times higher than white women. These disparities highlight the urgent need for equitable healthcare policies.
Why has the U.S. witnessed a rise in postpartum maternal deaths in recent years?
Postpartum maternal deaths in the U.S. have increased, potentially due to a lack of comprehensive postpartum care and the recognition that many health issues persist beyond the traditional six-week follow-up. An understanding of the full year post-pregnancy is crucial for improving maternal health outcomes.
What are preventable maternal deaths and why are they significant?
Preventable maternal deaths, which account for over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., signify that many fatalities could be avoided through better healthcare practices and innovations. Addressing these preventable causes is critical for reducing overall maternal mortality rates.
How do the trends in U.S. pregnancy care affect maternal mortality rates?
Trends in U.S. pregnancy care have significantly contributed to rising maternal mortality rates, reflecting a need for improved prenatal services and extended postpartum care. The COVID-19 pandemic has also exacerbated these challenges, highlighting the importance of addressing healthcare access and quality.
What initiatives can reduce maternal health disparities and improve outcomes?
Initiatives aimed at promoting equitable healthcare access, enhancing maternal health education, and increasing investment in innovative care solutions are essential for reducing maternal health disparities. Fostering collaborations between state health systems can also lead to better maternal health outcomes.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Rates of Maternal Mortality | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with rates increasing over the last four years. |
| Preventability of Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are considered preventable. |
| Disparities in Mortality | Significant racial and ethnic disparities exist: American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest rates, followed by non-Hispanic Black women. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest rate increase occurred in 2021, likely due to the pandemic. |
| Main Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, reflecting changing health trends. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and 1 year postpartum, highlighting the need for extended postpartum care. |
| Need for Healthcare Improvement | Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions is crucial to improve maternal health outcomes. |
Summary
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. have continued to rise despite the significant preventability of such deaths. The United States exhibits the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income nations, fueled by disparities linked to race and ethnicity. A focus on improving prenatal care and extending postpartum healthcare services is essential to address the alarming trends and ensure that preventable deaths are significantly reduced. To mitigate the ongoing crisis of maternal mortality, a robust public health infrastructure and tailored interventions are critical for equitable and effective maternal care.