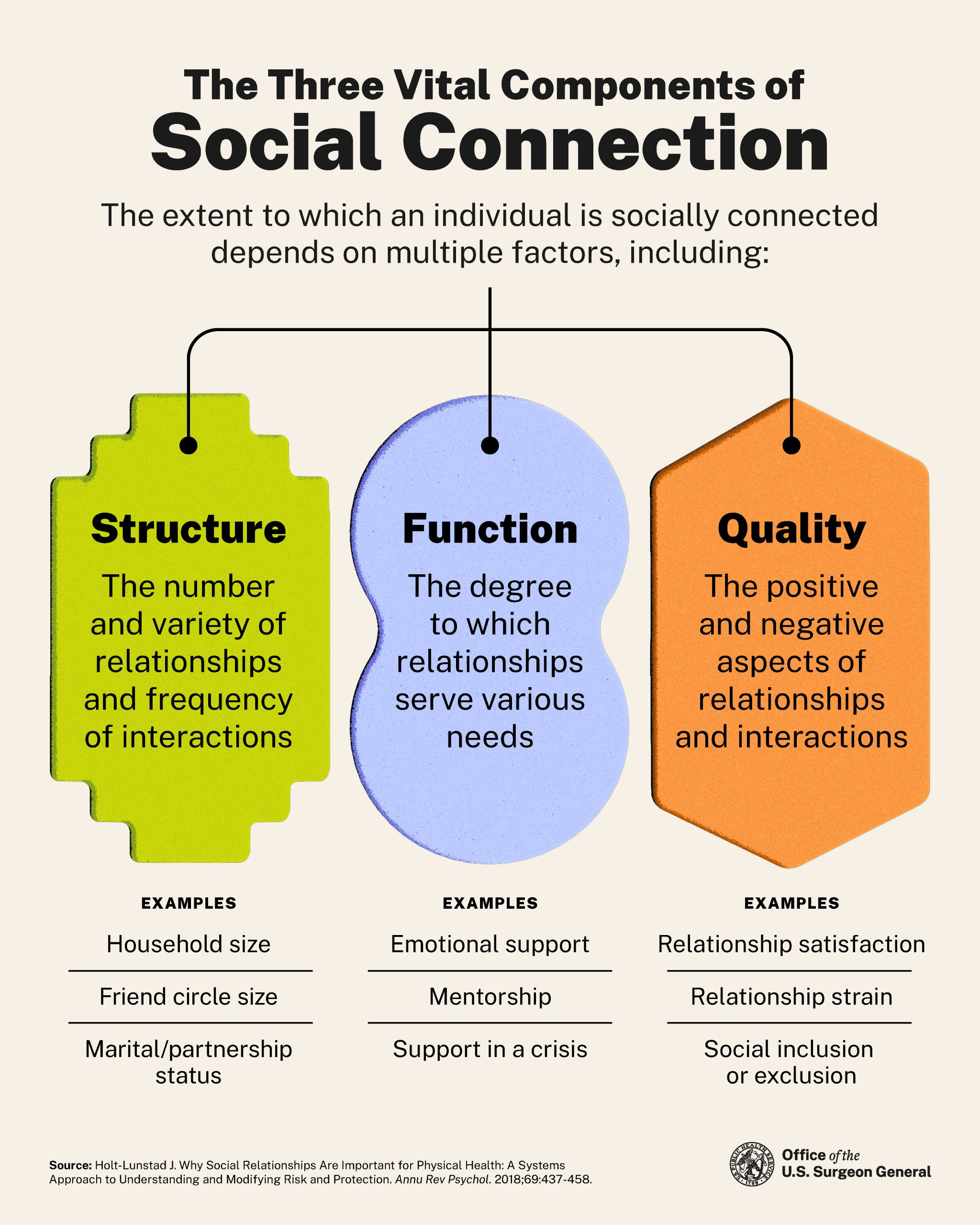
Social connection needs are an essential aspect of human existence, paralleling our basic requirements for food and water. Recent research has shed light on the neurological basis of social needs, revealing how deeply our brains are wired for interaction. The importance of social interaction cannot be overstated, as it plays a critical role in mental health and emotional well-being. On the contrary, the effects of social isolation can severely impact individuals, exacerbating issues like anxiety and depression. In this context, understanding the complex interplay between social behavior and neurological processes highlights the significant role of social connectivity in sustaining overall health.
Human social necessities, akin to our fundamental survival instincts, encompass the innate desire for companionship and connection. A wealth of research on social behavior underscores the vital importance of maintaining robust relationships, which directly correlates with one’s mental wellness. The ramifications of social disconnection are profound; loneliness often leads to detrimental health outcomes, emphasizing the need for communities to foster interpersonal interactions. Additionally, the neurological foundations behind these social urges reveal intricate systems within the brain that dictate our drive for connection. As we navigate modern life, recognizing the manifold layers of social engagement will illuminate its crucial role in enhancing our collective quality of life.
The Neurological Basis of Social Needs
Recent research has increasingly revealed the neurological underpinnings of our social needs, suggesting that our brains are wired to seek social interaction just as they are to pursue essential resources like food and water. The study led by Ding Liu highlights how the hypothalamus, a brain region known for regulating basic physiological drives, plays a crucial role in mediating social behavior. This indicates that social connection is integrated within the same neural circuits that control hunger and thirst, emphasizing its importance to human survival and well-being.
Understanding the neurological basis of social interaction can shed light on distressing issues such as social isolation. When individuals experience loneliness, the same areas of the brain may be activated as during physical pain, indicating that the effects of social isolation are profound and can adversely affect mental health. The research suggests that our need for social connectivity is not merely a want but a fundamental biological need, highlighting its vital role in maintaining psychological balance and emotional health.
Importance of Social Interaction for Mental Well-Being
Social interactions significantly contribute to mental health, evidenced by the growing recognition of their importance among health professionals. The U.S. Surgeon General’s assertion that social isolation is a pressing public health issue underscores the dire consequences of lacking social contact. Studies demonstrate that regular social interaction can lead to decreased symptoms of anxiety and depression and enhance overall life satisfaction. This finding points to the necessity of fostering environments where social bonds are prioritized.
Moreover, understanding that social connectivity can influence mental health outcomes significantly shifts how we approach mental health interventions. Programs designed to facilitate social interaction and integration can serve as complementary treatments for various mental health disorders. By emphasizing community support and creating opportunities for meaningful connections, health practitioners can provide a holistic approach to mental wellness.
Effects of Social Isolation on Health
The detrimental impacts of social isolation are well-documented, with effects ranging from diminished mental health to a decreased lifespan. Research indicates that extended periods of isolation can lead to severe consequences, such as increased rates of anxiety, depression, and even cognitive decline. The phenomenon is particularly alarming in the context of contemporary society, where social media and technology, while connecting people virtually, may inadvertently contribute to feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Additionally, studies indicate that individuals experiencing chronic social isolation are at a higher risk for various health complications, including cardiovascular diseases and weakened immune responses. Thus, addressing the pervasive issue of isolation is critical for public health initiatives, as improving social connectivity can lead to significant health benefits across populations.
Social Connectivity and Mental Health
The relationship between social connectivity and mental health is profound, as evidenced by rising research linking social behavior to psychological well-being. Engaging in social activities stimulates neurotransmitters such as oxytocin and dopamine, which are essential for mood regulation and feelings of happiness. Therefore, promoting social interactions can be a powerful tool in combating mental health issues, enhancing the quality of life for many individuals.
Incorporating social support into treatment plans is increasingly recognized as a vital aspect of mental health care. By encouraging patients to build and maintain social connections, therapists and health professionals can enhance therapeutic outcomes. This approach underscores the psychosocial dimensions of health, where fostering community relationships can serve as a protective factor against the onset of mental illnesses.
Research on Social Behavior: Insights into Human Interaction
Research dedicated to understanding social behavior reveals invaluable insights into human connections and interactions. Investigating the mechanisms behind social seeking and avoidance behaviors provides a deeper comprehension of how individuals form relationships and navigate social landscapes. Recent studies fuel the understanding that social behavior is not solely contingent on personal desires but is intricately linked to biological imperatives.
Moreover, such research enables scientists and psychologists to identify significant factors that can influence social engagement or withdrawal. By exploring various environments and stimuli that promote or hinder social interaction, we can unearth fundamental principles that drive social behavior, paving the way for interventions aimed at improving social connectivity in populations vulnerable to isolation.
Understanding the Role of Touch in Social Connectivity
Touch plays a crucial role in modulating social interactions, heavily influencing our emotional connections with others. Studies have shown that tactile experiences, such as hugging or hand-holding, can release hormones that improve mood and promote feelings of trust and safety. This scientific understanding underscores the importance of physical touch in establishing and strengthening social bonds, particularly in an era where virtual interactions are increasingly prevalent.
As highlighted in Liu’s research, the absence of physical touch due to social isolation can significantly impair our ability to connect with others. This lack of sensory feedback may lead to feelings of loneliness and depression, emphasizing the need to maintain touch-based interactions wherever feasible. The applications of this knowledge extend to therapeutic settings, where incorporating touch in therapy can improve patient outcomes, illustrating the value of multi-sensory approaches in promoting mental health.
Social Connection: A Fundamental Human Need
The assertion that social connection is a basic human need parallels our physiological requirements for essential resources. Just as food, water, and shelter are vital for survival, social bonds are essential for emotional and psychological health. This perspective encourages a reevaluation of how we prioritize social engagement within personal and community health frameworks, reinforcing the notion that nurturing relationships should be considered alongside traditional health measures.
Recent studies underscore that social bonds can lead to lower stress levels, improved mood, and overall better health outcomes. Recognizing social connection as a fundamental need compels policymakers, educators, and healthcare professionals to create supportive environments that foster interconnectedness. Ensuring individuals have the opportunity to engage socially can alleviate the burden of mental health issues exacerbated by loneliness, ultimately enhancing community resilience.
The Impact of Virtual Interactions on Social Connectivity
In recent years, virtual interactions have transformed how people connect, especially in the wake of social distancing measures. While technology can help maintain connections, it often lacks the physical presence and intimacy that face-to-face interactions provide. Understanding how digital communication impacts social needs is crucial; while it offers convenience, it may also increase feelings of isolation when it substitutes for real-life interactions.
Research consistently shows that people often leave virtual interactions feeling disconnected, highlighting the importance of balancing online and offline socialization. Although platforms enable communication across distances, they cannot replace the psychological benefits derived from in-person connection. Addressing this balance is paramount for maintaining mental health, fostering environments where both types of interactions can coexist harmoniously.
Exploring the Science Behind Social Needs
Investigating the science behind social needs is essential for understanding the role of socialization in human behavior. The nuances of how our brains process social engagement reveal a complex landscape where emotional, cognitive, and physiological components converge. By delving into these mechanisms, researchers can uncover the factors that motivate social interaction and highlight its significance for personal development and emotional health.
The field is evolving rapidly, incorporating findings from neuroscience, psychology, and sociology to form a comprehensive picture of social behavior. This interdisciplinary approach is pivotal for advancing our understanding of social needs, paving the way for innovative strategies to enhance social connectivity across different populations. The ultimate goal remains to ensure that social connectivity is recognized as a pillar of a healthy and fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neurological basis of social connection needs?
Researchers have found that social connection needs are encoded in the brain through specific neural circuits, especially in the hypothalamus. This area not only regulates basic needs such as hunger and thirst but also governs the instinctive drive for social interaction. Understanding this neurological basis helps to underscore the fundamental importance of social interactions for mental health.
How do social connection needs impact mental health and well-being?
Social connection needs play a crucial role in maintaining mental health. Meaningful social interactions can alleviate symptoms of mental illnesses like depression and anxiety. Conversely, social isolation can worsen these conditions, leading to a cycle of negative emotional experiences. Strong social ties provide support, reduce feelings of loneliness, and enhance overall well-being.
What are the effects of social isolation on individuals?
Social isolation has significant negative effects, similar to deprivation of other basic needs. It can lead to increased feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression, significantly impacting mental health. Studies reveal that prolonged isolation can even alter the way individuals respond to social settings, potentially fostering social aversion rather than connection.
Why is the importance of social interaction emphasized in health discussions?
The importance of social interaction is increasingly recognized in health discussions due to its profound impact on mental and physical well-being. Social interactions are linked to emotional regulation, stress relief, and even the promotion of physical health through community support systems. Health professionals advocate for addressing social needs alongside traditional health metrics.
What research highlights the connection between social behavior and basic human needs?
Recent research, including a study published in *Nature*, explores the similarities between social behavior and physiological needs like hunger and thirst. By studying neural mechanisms in the brain, researchers reveal how the drive for social interaction may stem more from a need to avoid negative emotions rather than solely seeking positive ones. Such insights offer new perspectives on the critical role of social bonds.
How can understanding social connection needs improve mental health interventions?
Recognizing the neurological basis and significance of social connection needs can enhance mental health interventions by promoting social skills development and community building. Understanding these needs enables tailored therapies that account for individual experiences with social isolation and fosters healthier relationships, ultimately leading to improved mental health outcomes.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Connection Needs | Social connection is considered a fundamental human need, similar to basic requirements like food and water. |
| Public Health Concern | The U.S. Surgeon General highlighted social isolation as a significant public health issue in 2023. |
| Neurological Basis | Research studies have identified the brain systems involved in wiring the need for social interaction. |
| Impact on Mental Health | Mental health issues like autism, depression, and schizophrenia show increased vulnerability to social isolation. |
| Mechanisms of Social Interaction | The research speculated that the urge for social engagement might be more about avoiding negative feelings rather than seeking positive ones. |
| Touch and Social Needs | Touch plays a critical role in fulfilling social needs, with implications for how we interact in an increasingly digital world. |
| Future Implications | Understanding social connection needs at a neurological level contributes to comprehending human behavior and improving mental health. |
Summary
Social Connection Needs are essential for human well-being, comparable to other basic necessities like food and shelter. Research highlights the neurobiological mechanisms underlying these needs, illustrating that social isolation can have detrimental mental health effects, similar to physical deprivation. As our interactions increasingly occur through technology rather than physically, understanding the intrinsic need for social connection becomes critical in fostering mental health and nurturing human relationships.