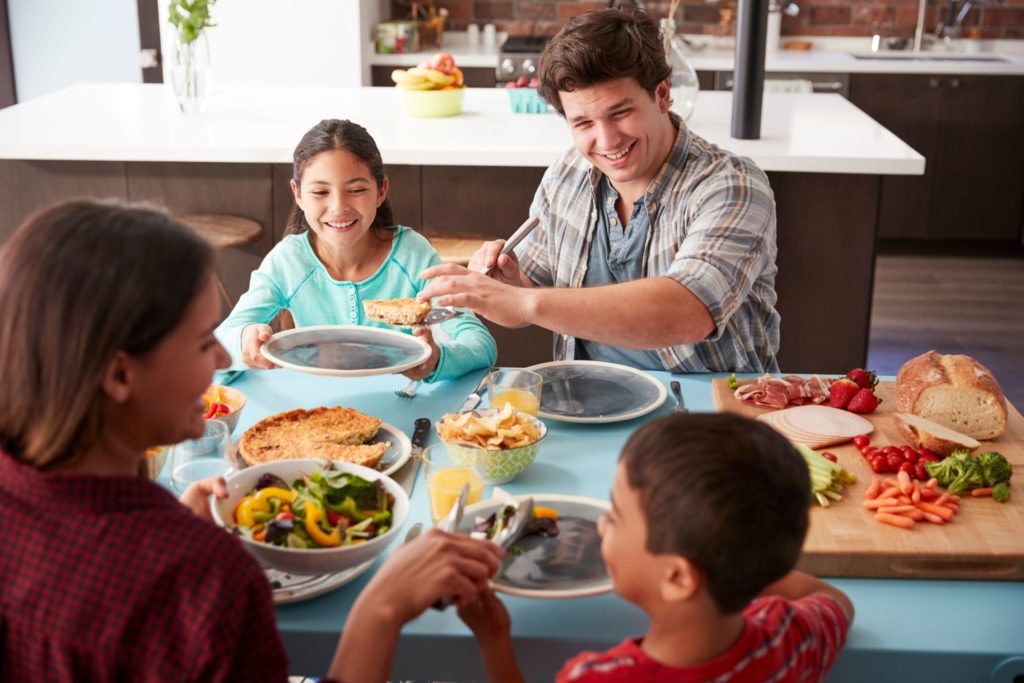
Shared meals and happiness form an intrinsic relationship that has been highlighted by recent research, which suggests that dining together can significantly boost well-being indicators. Studies show that people who frequently partake in communal meals report higher satisfaction with their lives and more positive emotions. The benefits of dining together are profound; not only do these shared experiences combat social isolation and happiness, but they also enrich our daily lives with meaningful interactions. In fact, happiness research indicates a growing correlation between meal sharing and emotional well-being, reinforcing the significance of these social gatherings. As Americans increasingly dine apart, understanding the importance of shared meals may be a crucial step toward enhancing overall happiness and health in our society.
The concept of collective dining and its effects on emotional wellness has garnered attention as more individuals explore the importance of enjoying meals with others. Engaging in communal feasts not only fosters a sense of belonging but enhances psychological health, impacting overall life satisfaction. With rising concerns about loneliness and the adverse effects of social disconnection, meal sharing’s role as a preventive measure against these issues is noteworthy. It can act as an antidote to the growing trend of isolation, encouraging laughter, conversation, and the development of strong interpersonal bonds. As research continues to unfold, understanding the multi-faceted significance of sharing meals could prove vital to promoting both happiness and community cohesion.
The Importance of Shared Meals in Assessing Happiness
Shared meals have emerged as a significant marker of well-being, often more indicative than traditional metrics like income or employment status. According to recent studies, including those from the Harvard Kennedy School, individuals who dine together regularly report higher levels of life satisfaction and emotional positivity. This correlation is not just a fluke; it holds across various demographics, including ages, genders, and cultural backgrounds. Consequently, researchers emphasize that the act of eating with others may resonate deeply with inherent human needs for connection and community.
The annual World Happiness Report has identified meal sharing as a critical factor in happiness research, suggesting that the simple act of dining with others has profound implications for one’s mental well-being. Interestingly, the shift in American dining trends reflects a worrying rise in social isolation, as more individuals report eating alone. This change could signify a broader pattern of disconnection in society, making it crucial to explore how shared meals can counteract loneliness and serve as a remedy for the escalating mental health concerns many face today.
Dining Together Benefits: More than Just a Meal
Dining together fosters a sense of community, providing benefits that extend beyond the meal itself. When individuals share food and conversation, they engage in social interactions that can strengthen relationships and build support networks. These exchanges play a vital role in enhancing overall happiness and can mitigate the effects of social isolation. Furthermore, studies highlight those who regularly share meals tend to be more optimistic and emotionally resilient, showcasing the powerful impact of communal dining on mental health and well-being.
Moreover, the significance of shared meals in promoting well-being cannot be understated. Engaging in regular meals with friends and family can trigger positive emotions and reinforce feelings of belongingness, creating a fertile ground for personal happiness. In a world increasingly characterized by loneliness, prioritizing communal dining may serve as a straightforward yet effective way to improve social connections and overall life satisfaction.
Well-being Indicators: Meal Sharing as a Reliable Metric of Happiness and Health
The research indicates that shared meals can serve as a trustworthy indicator of an individual’s sense of well-being. While traditional measures like income and job status remain important, they often fail to capture the depth of a person’s happiness. In contrast, meal sharing is a clear-cut, easily measurable activity that can offer insights into social bonds and emotional health. For example, data from the American Time Use Survey reveals a troubling rise in the number of individuals who eat alone, suggesting a potential decline in social cohesion and happiness.
This shift raises essential questions about how we can better understand and promote well-being in society. As researchers like Micah Kaats assert, knowing how many meals someone has shared can be far more revealing about their happiness than monetary factors alone. Understanding meal sharing as a key well-being indicator could inform public policy, encouraging programs that facilitate social interactions and community building through shared dining experiences.
The Link Between Social Isolation and Happiness in Meal Sharing
The diminishing number of shared meals correlates notably with rising social isolation in various demographics. As the data indicates that more individuals, particularly younger generations, are dining alone, this trend raises significant concerns about the long-term implications for happiness and mental health. Social isolation not only deprives individuals of meaningful interactions but has also been linked with various negative health outcomes, reinforcing the vital role that meal sharing plays in fostering connections and promoting joy.
Research indicates a cyclical relationship between social isolation and happiness, where an increase in solitary dining can perpetuate feelings of loneliness. On the other hand, those who actively engage in shared meals with friends and family often report a greater sense of fulfillment and happiness. Therefore, addressing social isolation through community-focused dining initiatives could be a pivotal strategy in enhancing overall public health and well-being.
The Role of Happiness Research in Promoting Shared Meals
Happiness research has increasingly spotlighted the importance of shared experiences, including dining together, as critical for emotional well-being. The correlation between shared meals and happiness presents a compelling case for prioritizing these social gatherings in our daily lives. As studies continue to emerge, they provide evidence that happiness is not merely an individual pursuit but rather a collective experience that thrives in communal settings. Researchers hope that by emphasizing the significance of meal sharing, we can develop actionable insights for enhancing social interactions.
Moreover, the insights garnered from happiness research can guide policymakers in structuring community initiatives aimed at fostering shared meals. By creating environments that encourage dining together, such as community kitchens or organized meal-sharing events, we can strengthen social ties and improve overall mental well-being. As the research unfolds, it becomes increasingly clear that investing in shared meals could yield substantial benefits for societal happiness.
The Future of Dining Together and Mental Health Solutions
Looking ahead, the relationship between shared meals and mental health presents an exciting frontier for research and public health initiatives. With escalating concerns around mental health, exploring how communal dining can serve as a preventative strategy is critical. By focusing on shared meals, we not only address the surface issue of social isolation but also delve into promoting happiness at a community level, fostering environments where emotional connections can flourish.
Considering the data revealing a rise in individuals eating alone, efforts to create spaces for shared meals could significantly enhance social well-being. These initiatives could range from policy interventions to community programs aimed at bringing people together around food. Ultimately, tackling mental health challenges through the lens of social connections, particularly dining together, reflects a holistic approach to improving population well-being and happiness.
Exploring the Emotional Benefits of Meal Sharing
The emotional benefits of sharing meals extend beyond mere consumer experience; they encapsulate communal bonding and shared happiness. When families, friends, or even colleagues gather to eat, it provides a unique opportunity to bond over food, laughter, and conversation. This interaction not only supports individual happiness but can also reinforce social ties, making meal sharing a unique channel for emotional support.
These gatherings serve as a reminder of the shared human experience, where joys and challenges are exchanged, often leading to deeper connections. By prioritizing shared meals, individuals can enhance their emotional resilience and contribute positively to their social networks, leading to improved mental health outcomes and greater overall happiness.
Policy Implications of Promoting Shared Meals
Understanding the connection between shared meals and happiness opens avenues for significant policy implications. As policymakers grapple with rising rates of social isolation and mental health issues, prioritizing initiatives that promote communal dining could yield beneficial societal outcomes. By funding community meal programs, encouraging family dining through educational campaigns, and creating public spaces designed for social eating, governments can help combat the isolation that many Americans face.
Such initiatives have the potential to bolster community ties, enhance social networks, and ultimately lead to happier, healthier populations. Recognizing meal sharing as a public health strategy could transform approaches to mental well-being, illustrating a proactive rather than reactive stance towards mental health challenges.
Culinary Traditions as Gateways to Happiness
Culinary traditions play a critical role in accessing the deep connections associated with shared meals. Different cultures around the globe have their unique ways of celebrating connections through food, showcasing the universality of shared dining as a source of happiness and social cohesion. Engaging with these culinary traditions not only enhances the dining experience but also empowers individuals to relive cultural identities that foster a sense of belonging and community.
As we appreciate the significance of these culinary practices, we can leverage them to foster environments where shared meals become a cornerstone of social interaction. By embracing diverse dining traditions, we enhance both communal ties and happiness, underscoring the importance of food in uniting people across various backgrounds.
The Science Behind Meal Sharing and Emotional Well-Being
The empirical research supporting the relationship between meal sharing and emotional well-being has garnered attention in the field of psychology. Studies have shown that individuals who participate in regular shared meals experience heightened levels of happiness and satisfaction, which researchers attribute to the effects of social interaction. These scientific findings are essential for understanding how communal dining fosters mental health, illustrating the profound psychological benefits that stem from simply sharing food with others.
Moreover, understanding the science behind meal sharing offers a unique perspective on how emotional well-being can be nurtured through simple, everyday actions. Fostering an awareness of these connections can inspire individuals to look to their dining habits as a means of enhancing their emotional health and creating rewarding social experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do shared meals relate to happiness and well-being?
Shared meals have been shown to significantly correlate with happiness and well-being. Research indicates that individuals who frequently dine together are more likely to report higher levels of life satisfaction and positive emotions. This relationship is so strong that shared meals are considered just as predictive of happiness as income or job status.
What are the benefits of dining together in terms of happiness?
Dining together fosters social connections and reduces feelings of social isolation, which are crucial for individual happiness. The act of sharing meals not only promotes bonding and communication but also releases hormones associated with well-being, further enhancing feelings of joy and fulfillment.
Is social isolation affecting happiness due to reduced shared meals?
Yes, research highlights an alarming trend of increased social isolation, with many individuals reporting that they dine alone more often. This rise in solitary meals is linked to lower happiness levels and may indicate a decline in social ties, which are essential for emotional well-being.
How does happiness research link meal sharing to positive emotions?
Happiness research suggests that sharing meals can improve emotional states by creating opportunities for dialogue and connection. Positive experiences during shared meals contribute to a greater sense of community and belonging, which are vital components of overall happiness and well-being.
What is the significance of meal sharing in happiness research?
The significance of meal sharing in happiness research is profound, as it provides a tangible measure of social interaction that can be linked to well-being. Unlike more abstract measures such as income, counting the number of meals shared is a straightforward way to gauge social connectivity, illustrating its impact on an individual’s happiness.
Can increasing the number of shared meals improve happiness levels?
While further research is needed to definitively establish causation, many experts believe that increasing shared meal experiences could enhance happiness levels. As communal dining promotes social bonding and reduces isolation, it stands to reason that fostering more meals together could lead to greater emotional well-being.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Shared Meals and Happiness | Shared meals are a significant predictor of well-being, as indicated by studies linking meal sharing to life satisfaction and positive emotions. |
| Income vs. Meal Sharing | The correlation between shared meals and happiness is comparable to that of income and employment status. |
| Decline in Shared Meals | Recent data show that 1 in 4 Americans are dining alone, a 53% increase since 2003, with a notable decline in shared meals among younger people. |
| Further Research Needed | It remains uncertain whether shared meals cause happiness or if happier individuals tend to share meals more frequently. |
| Simplicity of Measurement | Asking about shared meals is a straightforward method to gauge social connections compared to measuring income. |
| Policy Implications | Encouraging shared meals could serve as an effective intervention to improve social well-being amidst rising mental health and isolation issues. |
Summary
Shared meals and happiness are intricately linked, as research shows that dining with others significantly enhances our sense of well-being. This connection highlights the importance of fostering social interactions through meal sharing, especially in a time when loneliness and mental health issues are on the rise. The findings suggest that prioritizing shared meals can lead to increased happiness and satisfaction in life, making it a crucial factor for individuals and policymakers alike to consider in efforts to improve community well-being.